This website uses cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website. Learn more
To evaluate embryonic viability, it is first important to determine the developmental window of lethality as it can provide valuable information about the type of defects present in the embryos and/or placentas. To determine the window of lethality, representative stages will be chosen to dissect the embryos or fetuses. These stages represent critical time points in development and the results will help inform subsequent histological analyses. The embryos are sampled for macroscopical analyse and viability at times throughout pregnancy with focus on development of particular organs between E9.5 and E18.5.
To dissect embryos/fetuses at precise stages, parents intercrosses are followed rigorously to check the vaginal plugs (formed by the polymerization of proteins derived from prostatic secretions) each morning. The morning at which a vaginal plug is noted corresponds to the stage 0.5 dpc (days post-coïtum) or E0.5 (Embryonic day 0.5). Embryos and fetuses will be genotyped by using extraembryonic membranes (yolk sac) or tail pieces, respectively.
For statistical reasons, at least 28 embryos have to be dissected and genotyped for one developmental stage in order to know if the line is lethal, viable or subviable. This corresponds to the dissection of four pregnant females (7 pups/female approximately).
To detect developmental defects in prenatal mice from E5.5 to E18.5. Embryos and fetuses are analyzed macroscopically, then fixed in Bouin's fluid, decalcified (for ages E16.5 and beyond), embedded in paraffin, serially sectioned at 7 µm and stained with hematoxylin and eosin or Mallory's trichrome and hematoxylin stain. Whole skeletal analyses can be performed on E18.5 fetuses (alcian blue and alizarin red staining)
Stereomicroscopes
Slide scanner (Nanozoomer 2.0 HT, Hamamatsu Photonics K.K., Hamamatsu City, Japan)
Microtomes
Cryostats
Always use age-matched littermates as controls
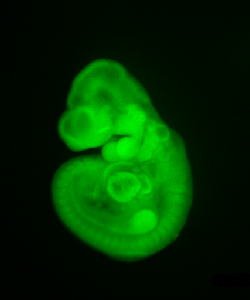
LacZ enzyme activity is evaluated by histochemical staining in order to characterize anatomical structures expressing the targeted gene in embryos carrying a lacZ transgene. See gene expression pattern.
Rapid three dimensional imaging of density-contrasted tissues (soft tissues) and non-contrasted tissues (skeletal elements) in the embryo using X-ray transmission and computed tomography.
The phenotyping of fetuses at later stages (E18.5) can use micron-scale X-rays Computed Tomography (μCT), which achieves a resolution of 10μm (isotropic voxel size) and allows the morphological analysis of organs in situ without dissection. To achieve sufficient contrast, formalin-fixed fetuses will be stained in Lugol’s iodine as a contrast agent. The impregnation of iodine in tissues will increase X-rays absorption due to iodine’s high atomic number and therefore enhance contrast in the resulting images. Obtained raw data have to be processed to facilitate direct comparison between samples.
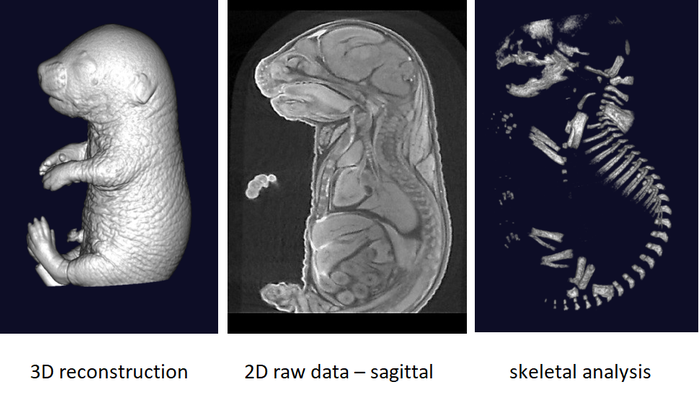
It is recommended to use at least 3 experimental embryos and one control embryo for analyse.
HREM is an effective and powerful tool for assessing structural abnormalities in embryos. Three dimensional reconstruction of embryo slices provides the definition of histological staining with the completeness of 3-D imaging.
HREM imaging is operated with a home made system (developed with the IGBMC Imaging Center)
1-The sample is fixed in Bouin’s solution
2-JB4 Resin embedding :
3-Samples limitations: the size must not exceed 1.5 cm3
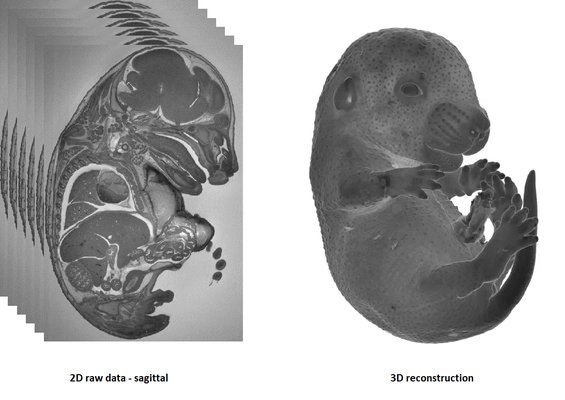
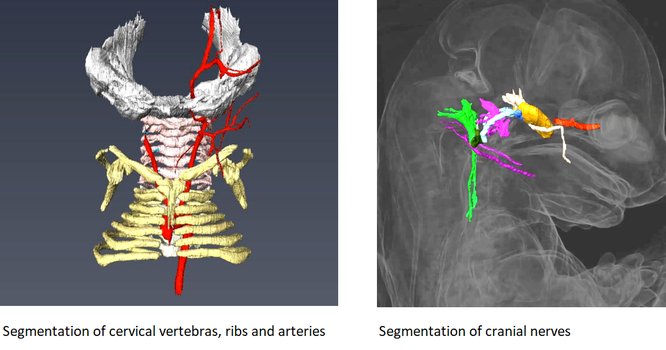
It is recommended to use at least 3 experimental and 3 control samples for analyse.
To better characterize primary defects of mutant embryos or to screen for abnormalities, vascular (PECAM), neural (neurofilament) markers are proposed. Other marker stainings can be developed on demand.